什么是OCP?
OCP是软件开发的七大开发原则:开闭原则
核心:其他6个原则的基础
OCP开闭原则核心是什么?
只要你在扩展功能的时候,没有修改以前写好的代码,那么就是符合OCP原则的,反之则违背了OCP原则
当系统功能拓展时,如果动了之前稳定的程序,修改了之前的程序。之前所有程序都需要测试,这是不想看到的
违背依赖倒置原则(DIP原则)
上依赖下就是违背:如:表示层依赖服务层,服务层依赖持久层
控制反转
一种编程思想。或设计模式
- 不在程序中采用硬编码方式来 new 对象
- 不在程序中采用硬编码方式来 维护对象关系
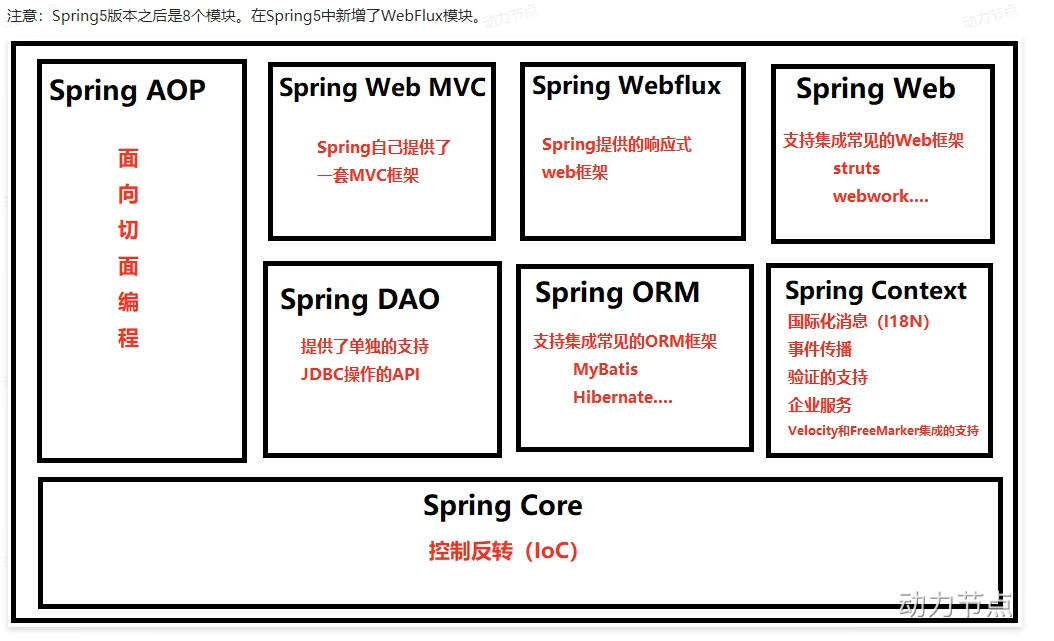
Spring框架
- Spring框架实现了控制反转IoC这种思想
- spring帮你new对象
- spring帮你维护对象关系
- Spring 时一个实现了IoC思想的容器
- 依赖注入的两种方式(依赖注入时现实IoC的具体实现: XML解析+工厂模式+反射机制)
- set 注入(执行set给属性赋值)
- 构造方法 注入(执行构造方法给属性赋值)
- 依赖注入的两种方式(依赖注入时现实IoC的具体实现: XML解析+工厂模式+反射机制)
创建一个spring6项目
创建一个普通maven项目
添加spring6的依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- 当你引入 Spring Context依赖后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.5</version>
</dependency>配置spring 配置文件 xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- IDE工具提供了这个模板 -->
<!-- 配置bean,这样spring会帮我们管理这个对象
bean标签的两个重要属性
id: 全局唯一
class: 需要关系的类的全路径
-->
<bean id="userBean" class="com.spring.bran.User" ></bean>
</beans>新建 com.spring.bran.User 类
1
2
3
4
5package com.spring.bran;
public class User {
}测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public void testUserBean() {
// 第一步:获取spring 容器对象
// ApplicationContext 有很多实现类 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext用来专门加载spring 配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
// 第二步:根据bean id 从 spring 容器中获取这个对象
// 返回值是一个对象,可以传第二个参数设置类型
Object userBean = applicationContext.getBean("userBean", "User.class");
System.out.println("userBean = " + userBean);
}
// 非类路径下获取配置文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext fs = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("d://xxx.xml");
spring 启用 Log42 日志框架
引入依赖
1 | <!-- log4j依赖 --> |
配置文件名字必须是 log4j2.xml
1 |
|
此时已经启用
自己怎么使用log4j2记录日志?
1 |
|
依赖注入
service 层引用了 Dao层对象,怎么配置让spring自动生成
基于set方法的依赖注入
dao.UserDao
1 | public class UserDao { |
service.UserService
1 | public class UserService { |
配置 bean
1 | <bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" ></bean> |
测试
1 | // app 为spring容器对象 |
基于构造方法的依赖注入
service.UserService
1 | public class UserService { |
配置bean
1 | <bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" ></bean> |
内/外部注入 bean
内部 bean 就是在 property 里面使用 bean标签的方式,效果跟上面一样, 一般不用
1 | <bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" ></bean> |
简单类型注入
UserDao 中提供成员属性 username,password 的set,get方法
1 | <bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" > |
哪些类型被认为是简单类型?
BeanTuils.java 中的isSimpleValueType 方法 中经行了描述
- 8中基本类型及其包装类
- 字符串
- 枚举
- class
- 日期 Date,Temporal
日期直接传字符串会导致报错,它要求指定的日期格式字符串。比较麻烦,一般不把它当作简单类型处理
经典应用场景
数据源 都实现了 DAtaSource 接口,其中的获取 connection 对象时要传入 driver,url,username,password 时可以采用配置 注入
1 | <bean id="myDataSource" class="xxx"> |
级联属性赋值
使用级联属性必须要有 get方法,在一个bean中给另一个bean赋值属性
1 | // 学生bean中给班级类注入数据 |
数组注入
数组简单数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10<bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" >
<property name="strArray">
<array>
<value>值1</value>
<value>值2</value>
<value>值3</value>
<value>值4</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>数组 引用类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21<bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" >
<property name="girlFriends">
<array>
<ref bean="girlFriend1" />
<ref bean="girlFriend2" />
<ref bean="girlFriend3" />
</array>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="girlFriend1" class="com.spring.bean.dao.Woman" >
<property name="name" value="小花" />
<property name="age" value="18" />
</bean>
<bean id="girlFriend2" class="com.spring.bean.dao.Woman" >
<property name="name" value="小丽" />
<property name="age" value="20" />
</bean>
<bean id="girlFriend3" class="com.spring.bean.dao.Woman" >
<property name="name" value="小婉" />
<property name="age" value="22" />
</bean>
注入集合
list 集合有序可重复,无需不可重复。元素时基本类型用value,引用类型用<ref bean=”” />
1 | <property name="names"> |
map 集合
1 | <property name="addrs"> |
注入一个 null, 空字符串
要注入一个 null. 要不就不写这条属性注入,要不就如下:
1 | <property name="name" > |
注入空字符串
1 |
|
注入 特殊字符
使用实体符号:如
1 | // 报错 |
使用 <![CDATA[]]>
1 | <property name="rs"> |
基于p命名空间的注入
p命名空间注入基于 set 方法,用来简化传值操作
c命名空间注入基于构造 方法,用来简化传值操作
1、在spring 的配置文件头部添加p命名空间。
2、使用
2
3
4
// 将日期对象作为引用类型传入
<bean id="birthBean" class="java.util.Ddate"></bean>
util 命名空间注入
让配置复用,主要针对集合
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
"
<util:list id="ml" >
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>张三</value>
</list>
</util:list>
<bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" >
<property name="anyList" ref="ml" />
</bean>
基于XML自动装配
根据名字自动装配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// 之前写法
<bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao" ></bean>
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.spring.bean.service.UserService" >
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoBean" ></property>
</bean>
// 自动装配
// 此处bean的名字应是set方法名不带set的小驼峰,此外自动装配是set注入,不要重写有参构造方法
<bean id="userDao" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao"></bean>
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.spring.bean.service.UserService" autowire="byName" ></bean>根据类型自动装配
1
2
3<bean id="userDao" class="com.spring.bean.dao.UserDao"></bean>
// 这也是 set注入的方式,同种类型参数不要超过两个
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.spring.bean.service.UserService" autowire="byType" ></bean>
spring 引入外部属性文件
以前 mybatis 通过 配置文件 设置properties.resource引入外部属性文件
现在spring中:
1、先引入 context 命名空间
1 | xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" |
2、使用标签引入
注意,xxx.properties 文件的属性在命名时 加上前缀 如:jdbc.username=root. 否则可能会优先读取电脑全局属性username:结果是 Administrator
1 | <context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties" ></context:property-placeholder> |
bean 作用域
spring 默认情况下如何管理这个Bean的?
默认情况下 Bean是单例的,在Spring初始化的时候实例化,所以每次调用getBean(),都返回那个单例对象
我们可以通过设置Bean标签的属性scope来改变Bean是否为单例(singleton)/多例(prototype)。web项目会有更多配置
自定义 scope
1 | <!-- 配置我们自定义的作用城--> |
使用
1 | <bean id="xxx" scope="threadScope" /> |
效果:在不同线程下,getBean 获取的对象不一样。是线程安全的
Bean 的实例化(获取)方式
通过构造方法实例化
在文件中写 Bean 标签,spring 会自动调用该类构造函数实例化 Bean
通过简单工厂模式实例化
通过简单工厂模式。spring会到 StarFactory 类中 调用 get 获取实例对象
1
<bean id="startBean" class="com.xxx.bean.StarFactory" factory-method="get" />
1
2
3
4
5
6
7public class StarFactory {
// 静态方法
public static Star get() {
// 返回Star 对象实例
return new Star();
}
}通过factory-bean实例化
通过工厂方法模式。通过 factory-bean,factory-method 属性共同完成
1
2<bean id="gunFactory" class="com.xxx.bean.GunFactory" />
<bean id="gun" factory-bean="gunFactory" factory-method="get" />GunFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7public class GunFactory {
// 实例方法
public Gun get() {
// 实际上 new 这个对象还是我们程序员自己 new 的
return new Gun();
}
}Gun
1
2
3
4
5public class Gun() {
public Gun() {
System.out.println("Gun的无参构造方法执行");
}
}通过 FactoryBean 接口实例化
实际上是第三种方法的简化
PersonFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public class PersonFactory implements FactoryBean {
public boolean isSingleton() {
// 是否单例
return true;
}
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return new Person();
}
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
}Person
1
2
3
4
5
6public class Person {
public Person() {
System.out.println("执行构造函数!");
}
}spring.xml
1
<bean id="person" class="com.xxx.PersonFactory" />
FactoryBean与BeanFactory区别?
FactoryBean 是 Bean 它是辅助spring创建其他bean的,而BeanFactory 是创建Bean的工厂,负责创建Bean对象
FeatoryBean 注入 Date 类型
Date 在 spring中被当作简单类型,
1 | public class DateFactory implements FactoryBean<Date> { |
1 | <bean id="dateBean" class="com.spring.bean.service.DateFactory" > |
Bean 的声明周期
粗略的五步走
- 实例化Bean,调用无参构造方法
- 给Bean属性赋值,set方法
- 初始化Bean。会调用Bean的init方法,这个方法需要自己写
- 使用Bean
- 销毁Bean,调用Bean的destroy 方法,这个方法也需要自己写
1 | // 指定生命周期函数 |
生命周期的七步。就是在第三步增加 before,after。怎么加呢?
编写一个类实现 BeanPostProcessor 类并重写 after,before方法
1 | public class SevenStep implements BeanPostProcessor { |
1 | // 作用域配置文件中所有Bean |
生命周期十步走
在BeanBefore 前后增加,和销毁之前增加
before前检查Bean是否实现了Aware相关接口,并设置相关依赖
2
implements BeanNameAware,BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAwarebefore后检查Bean是否实现了InitialzingBean接口,并调用方法
销毁前检查Bean是否实现了DisposableBean接口,并调用方法
Spring容器只对singLeton的Bean进行完整的生命周期管理
如果是scope = porototype 作用域的Bean,Spring容器只负责将bean初始化完,等客户端程序一旦获取到Bean之后,Spring容器就不再营理该对象的生命周期了.
将自己new的对象纳入spring容器管理
1 | // 自己 new 的对象 |
Bean 的循环依赖
A对象引用B属性,B对象引用A属性。相互引用
singleton + setter模式下的循环依赖是没有问题的。
本质原因:任意一个Bean实例化时,马上经行曝光,其他Bean可以引用它了,此时属性可能还没有注入。因为是单例,全局只有一个
prototype + setter 模式下循环依赖出现问题。当其中一个类型是 singleton 时就没问题
基于构造方法的注入模式下循环依赖会出现问题
spring IoC注解式开发
用来简写配置,避免编写xml文件
声明Bean的注解
1、使用注解需要AOP的依赖
2、配置context命名空间
2
3
4
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
"3、给spring框架开启扫描哪些包中的类
2
多个包用,隔开。也可以使用父包名4、在bean上使用注解
- @Component
- @Controller
- @Service
- @Repository
选择性实例化
方式1
1 | // 让所有属性失效 |
方式2
1 | <context:component-scan base-package="com.xxx.bean"> |
负责注入的注解
- @Value
- @Autowired
- @Qualifier
- @Resource
@Value
要注入属性类型是简单类型时,可以使用。
此方式注入不依赖set方法。可以用在属性上,构造方法形参上,set方法上
1 |
|
@Autowired 与 @Qualifier
@Autowired 可以注入非简单类型, 自动装配【默认是ByType】
如需按 名字注入需和 @Qualifier一起使用
此方式注入也不依赖set方法。可以使用在 成员属性,构造方法,构造方法形参
1 | // OrderDao.java |
@Resource
可以完成非简单类型注入。存在于jdk拓展包中(所以使用时需要额外引入),可理解为标准注解。而@Autowired 是spring框架自己的。
Resource注解可用在 属性上,setter方法上。
现根据类型装配,找不到就根据名字
引入依赖
1 | // spring5 |
使用
1 |
|
全注解开发
不使用配置文件,通过其他方式获取XML返回值
1 | // 之前 |
@Configuration
@Configuration用于定义配置类,可替换xml配置文件,被注解的类内部包含有一个或多个被@Bean注解的方法,这些方法将会被AnnotationConfigApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext类进行扫描,并用于构建bean定义,初始化Spring容器。
注意:@Configuration注解的配置类有如下要求:
- @Configuration不可以是final类型;
- @Configuration不可以是匿名类;
- 嵌套的configuration必须是静态类。
1 |
|
结论:
@Configuation等价于<Beans></Beans>
@Bean等价于<Bean></Bean>
@ComponentScan等价于<context:component-scan base-package=”com.ahies.ija.management”/>
JdbcTemplate
spring内置的对jdbc的简化操作方式。但实际项目中一般会使用mybatis
配置 JdbcTemplate
依赖
1 | <dependency> |
spring.xml
1 | <!-- 配置数据源 --> |
使用
1 |
|
GoF之代理模式
静态代理
需求:检测出所有Service业务方法的耗时时间
-硬编码:每个业务方法中直接添加计时代码
违背OCP开闭原则
-编写业务子类,继承业务类,对每个业务方法重写
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public void deleteXXX(id) {
// 开启计时
super(id);
// 结束计时
}
} 代码耦合度高,没有复用
-代理对象
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// 代理目标,代理接口,不要代理实现类
private FatherService target;
// 构造赋值
public FatherServiceProxy(FatherService targrt) {
this.target = targrt;
}
public void deleteXXX(id) {
// 开启计时
target.deleteXXX(id);
// 结束计时
}
}
// 创建目标
FatherService target = new FatherServiceImpl();
// 创建代理对象
FatherServiceProxy proxy = new FatherServiceProxy(target);
// 调用代理方法
proxy.deleteXXX("1"); 符合OCP原则,耦合度低.但是没有复用每个类都要新增一个代理类,类多
动态代理
还是代理模式,只是新增了字节码生成技术,动态生成代理对象。减少代理类的数量
动态代理技术:
- jdk内置动态代理 Proxy,只能代理接口
- CGLIB动态代理技术,是一个开源库,底层是继承方式继承。性能比jdk动态代理好(底层有个小儿快的字节码处理框架 ASM)
- javassist
jdk 动态代理
1 | // 要代理的接口 OrderService |
1 | public class TimerInvocationHandle implements InvocationHandler { |
CGLIB动态代理
1 | // 创建字节码增强对象 |
1 | public class TimerMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { |
面向切面编程
切面编程(AOP)底层就是通过动态代理来实现的,是OOP的补充和延申。
spring 的AOP 使用的代理是:jdk 的动态代理是+CGLIB动态代理技术。jdk代理接口,CGLIB代理类,自由切换,也可以设置只是用 CGLIB
具体使用场景,项目中日志模块,安全模块,事务模块,这些服务被称为交叉业务。它们都使用面向切面来实现
连接点 Joinpe
在程序的整个执行流程中,可以织入切面的位置。方法的执行前后,异常抛出之后等位置
切点 Pointcut
在程序执行流程中,真正织入切面的方法。本质就是方法。一个切点对应多个连接点
通知 Advice
通知就是增强代码,就是具体要织入的代码。根据放置的位置有不同名字
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知
切面 Aspect
切点 + 通知 就是 切面
织入
把通知应用到目标对象的过程
代理对象 proxy
一个目标对象被织入通知后产生的新对象
目标对象 Target
被织入通知的对象
切点表达式
切点表达式用来定义通知往哪些方法上切入
1 | execution([访问控制权限修饰符] 返回值类型 [全限定类名]方法名(形式参数列表) [异常]) |
访问控制权限修饰符
- 可选项
- 没写,就是4个权限都包括。
- 写public就表示只包括公开的方法
返回值类型
- 必填项。
- *表示返回值类型任意
全限定类名:
- 可选项
- 两个点”..”代表当前包以及子包下的所有类
- 省略时表示所有的类
方法名
- 必填项。
- *表示所有方法
- set*表示所有的set方法
形式参数列表
- 必填项
- 0表示没有参数的方法
- (..)参数类型和个数随意的方法
- (*)只有一个参数的方法
- (*,String)第一个参数类型随意,第二个参数是String的。
异常
- 可选项。
- 省略时表示任意异常类型
service包下所有的类以delete开始的所有方法
1 | execution(public * com.xxx.service.*.delete*(..)) |
使用spring 的AOP
- spring 框架结合Aspectj 框架 实现的AOP,基于注解方式
- spring 框架结合Aspectj 框架 实现的AOP,基于XML方式
- spring 框架自己实现的AOP(基本不用)
准备依赖:
2
3
spring-aop
spring-aspectsspring 配置context,aop命名空间
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/aop/spring-aop.xsd
"
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.bean.service" />
<!-- 开启aspectj 的自动代理
proxy-target-class: true 表示CGLIB动态代理,反之jdk动态代理
-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" />目标对象:
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class LoginService {
public void login() {
System.out.println("正在登录!");
}
}切面通知:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class LogAspect {
// 切面 = 通知 + 切点
public void beforeLogin() {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
}测试类:
2
loginService.login();
前置通知: @Before 目标方法执行之前的通知
后置通知:@AfterReturning 目标方法执行之后的通知
环绕通知: @Around 目标方法之前添加通知,同时目标方法执行之后添加通知
1 |
|
异常通知:@AfterThrowing 发生异常之后执行的通知
最终通知: @After 放在finally语句块中的通知
多个切面的执行顺序
给切面类添加注解 @Order(1)。 其中数字越小,执行越靠前
通用切点
1 |
|
AOP 之连接点
除了 环绕通知外,其他通知都可以接受 ( JoinPoint joinPoint ){}.\
通过 joinPoint 可以拿到 joinPoint签名 获取目标方法的信息
全注解方式开发
1 |
|
基于XML的方式开发
了解一下配置文件方式开发
配置文件:添加 aop,context 命名空间
1 | <bean id="loginService" class="com.xxx.LoginService"></bean> |
目标对象:
1 | public class LoginService { |
切面通知:
1 | public class LogAspect { |
编程式事务解决方法
1 |
|
AOP的实际案例:安全日志
项目开发结束,上线了。运行正常。客户提出新需求,凡是在系统中经行增删改操作的,都要把这个人的记录下来。因为这几个操作是危险的
切面
1 |
|
目标类
1 |
|
spring事务
编程式事务:通过编写代码的方式来实现
声明式事务:基于注解,基于XML两种方式
spring 底层通过AOP方式对事务进行了封装。所以spring专门针对事务开发了一套API
spring6中有他的两个实现
- DataSourceTransactionManager: 支持jdbcTemplate,Mybatis,Hibenate等事务管理
- JtaTransactionManager: 支持分布式事务管理
基于注解的事务管理:
配置任务管理器
1 | <!-- 创建事务管理器--> |
配置tx命名空间
1 | xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" |
开启事务注解
1 | <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven> |
使用
1 | // 在类上,方法上使用 |
注解参数详情(声明式事务管理参数配置)
1、propagation:事务的传播行为
当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用的时候,这个事务方法如何进行
事务的传播行为可以由传播属性指定,spring定义了7种类传播行为
- REQUIRED: 支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个默认)[没有就新建,有就加入]
- SUPPORTS: 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行[有就加入,没有就不管了]
- MANDATORY:必须运行在一个事务中,如果当前没有事务正在发生,将抛出一个异常[有就加入,没有就抛异常]
- REQUIRES NEW:开启一个的务,如果一个事务已经存在,则将这存在的事务挂起[不营有没有,直接开启一新务,开启的新事务和之前的事务不存在套关系,之前事务按起]
- NOT_SUPPORTED: 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务[不支持事务,存在就挂起]
- NEVER: 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常[不支持事务,存在就抛异常]如果外层事务不存在,行为就像REQUIRED一样]
- NESTED:如果当前正有一个事务在进行中,则该方法应当运行在一个嵌套式事务中。被嵌套的事务可以独立于外层事务进行提交或回滚。样。[有事务的话,就在这个事务里再嵌套一个完全独立的事务,嵌套的事务可以独立的提交和回滚。没有事务就和REQUIRED一样。]
1 |
2、ioslation:事务隔离级别
(1)事务有特性称为隔离性,多事务操作之间不会产生影响,不考虑隔离性产生很多问题
(2)不考虑隔离性则存在三个问题:脏读、不可重复读、虚(幻)读
(3)脏读:一个未提交事务读取到另一个未提交事务的数据
(4)不可重复读:一个未提交事务读取到另一个提交事务修改数据
(5)幻读:一个未提交事务读取到另一提交事务添加数据
(6)通过设置事务隔离性,解决读问题
3、timeout:超时时间
(1)事务需要在一定时间内(代码最后一条DML方法执行完加上之前的时间)进行提交,如果不提交则进行回滚
(2)默认值是-1,设定时间以秒为单位计算
4、readOnly:是否只读【里面不会执行增删改操作,设置后spring会启动优化策略,提高select语句执行效率】
(1)读:查询操作,写:添加修改删除操作
(2)readOnly默认设置为false,表示可以查询,可以添加修改删除操作
(3)设置为true后,只能查询
5、rollbackFor:回滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常进行事务回滚
6、norollbackFor:不回滚
(1)设置出现哪些异常不进行事务回滚
1 | // 出现 RuntimeException 异常或子类异常不回滚 |
全注解式事务开发
xml文件
1 |
|
注解文件
1 | // 代spring.xml配置文件,在这个类当中完成配置 |
使用
1 | ApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Config.class): |
基于XML的事务管理
但实际开发一般都是注解
1 |
|
Spring对Junit4 的支持
注解加载指定spring.xml
1 | // 从类路径加载 |
Spring对Junit5 的支持
1 | // spring 对junit支持的依赖 |
1 | // 从类路径加载 |
spring 集成 myBatis
1、依赖
- spring-context
- spring-jdbc
- mysq驱动
- mybatis
- mybatis-spring: mybatis提供的与spring框架集成的依赖
- 德鲁伊连接池
- junit
2、建包
- service
- AccountService
- service .impl
- AccountServiceImpl
- mapper
- AccountMapper
- pojo
- Account
3、配置 spring.xml
1 |
|
jdbc.properties
1 | jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver |
mybatis.xml
1 |
|
AccountMapper.xml
1 |
|
XML配置文件中引入外部XML
1 | <import resource="common.xml" /> |
- 本文作者: 王不留行
- 本文链接: https://wyf195075595.github.io/2023/02/17/programming/java/spring/
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 MIT 许可协议。转载请注明出处!


 LiYongci
LiYongci
 衔蝉
衔蝉
 哈希米
哈希米